Updated by Piper Wenzel, BS April 2024
See also: Sialolithiasis; Parotid Sialogram Stone; Submandibular gland stone removal sialendoscopy case example
- Around 85% of stones occur in the submandibular gland, around 15% occur in the parotid gland (Hammett 2022)
- Most common in the 3rd to 6th decades of life; males > females (Ashindoitiang 2023)
- Patients with stone(s) may have no symptoms or may present with painful swelling after meals (Ashindoitiang 2023)
- Risk factors for development include increased age, history of radiation therapy to head/neck, Sjogren's syndrome, medication affecting saliva production, decreased fluid intake (Ferneini 2021, Hammett 2022)
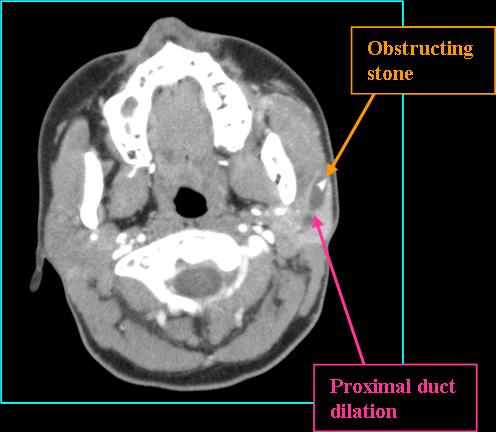
- ~ 80% of submandibular and 60% of parotid stones are visible on plain radiographic imaging (Friedman 2023)
- CT is highly sensitive for small stones not otherwise visible on plain film (Friedman 2023)
- Ultrasound may be used first-line in children and may diagnosis stones > 2mm (Friedman 2023)
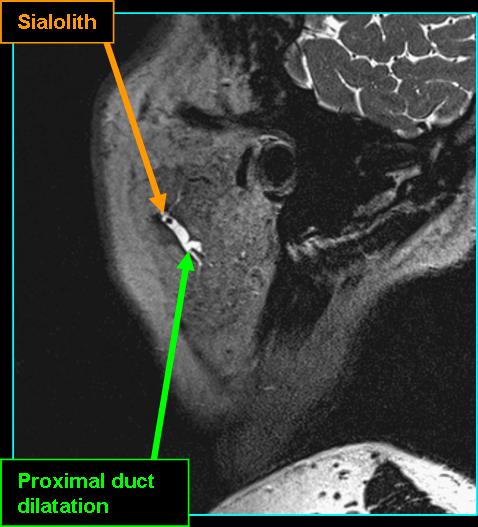
- MR sialography may diagnose radiolucent stones - may appear as a hypointense area in a dilated duct (Friedman 2023)
- Conservative measures may be taken initially including gland massage, NSAIDs, and sialogogues (Hammett 2022)
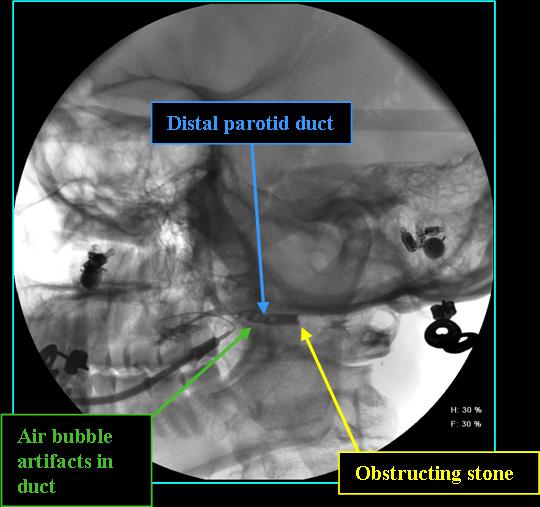
- If unreponsive to conservative treatment, further measures including endoscopy, transoral ductotomy, extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy, or duct and gland excision may occur (Hammett 2022)
![]()
![]()
![]()
References
Ashindoitiang JA, Nwagbara VIC, Ugbem T, Odoks RK, Udo Solomon A, Akpan SO, Ogamba N, Asuquo ME. Huge sialolith of the submandibular gland: a case report and review of literature. J Int Med Res. 2023 Jan;51(1):3000605221148443. doi: 10.1177/03000605221148443. PMID: 36624984; PMCID: PMC9834782.
Hammett JT, Walker C. Sialolithiasis. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; September 26, 2022.
Friedman E, Cai Y, Chen B. Imaging of Major Salivary Gland Lesions and Disease. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2023;35(3):435-449. doi:10.1016/j.coms.2023.02.007
Ferneini EM. Managing Sialolithiasis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2021 Jul;79(7):1581-1582. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2021.04.021. PMID: 34215413.